
It is recommended that you update your browser to the latest browser to view this page.
Please update to continue or install another browser.
Update Google Chrome
Description
| Qunitity | MRP |
|---|---|
| 60 capsules | 750/- |
Miraculous results in Arthiritis & Joint Pains
Our scientists have formulated a Phyto-Molecule based unique product, ARTHOKAR , It’s a combination of circumin, boswellia, ossimumsenctum, and more that create miracle results in joints pain.
What is Arthritis? skeleton of a man with joint pain. The term "arthritis" is used to describe numerous rheumatic diseases and conditions that affect joints. Rheumatic conditions are typically characterized by pain, aching, stiffness and swelling in and around one or more joints. The symptoms can develop gradually or suddenly. Certain rheumatic condition can also involve the immune system and various internal organs of the body.
Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, can affect multiple organs and cause widespread symptoms.
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the body's immune system attacks the tissues of the body, specifically connective tissue, leading to joint inflammation and pain and degeneration of the joint tissue.
ARTHOKAR is a unique blend of highly effective and rarely available herbs. It removes the cause and effect of arthritis as well as it repairs the damaged cartilage or any joint pain. Just by taking one capsule.
Fast Facts On Arthritis
Arthritis is very common but is not well understood. Actually, “arthritis” is not a single disease; it is an informal way of referring to joint pain or joint disease. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis and related conditions. People of all ages, sexes and races can and do have arthritis, and it is the leading cause of disability in America. More than 50 million adults and 300,000 children have some type of arthritis. It is most common among women and occurs more frequently as people get older.
Common arthritis joint symptoms include swelling, pain, stiffness and decreased range of motion. Symptoms may come and go. They can be mild, moderate or severe. They may stay about the same for years, but may progress or get worse over time. Severe arthritis can result in chronic pain, inability to do daily activities and make it difficult to walk or climb stairs. Arthritis can cause permanent joint changes. These changes may be visible, such as knobby finger joints, but often the damage can only be seen on X-ray. Some types of arthritis also affect the heart, eyes, lungs, kidneys and skin as well as the joints.
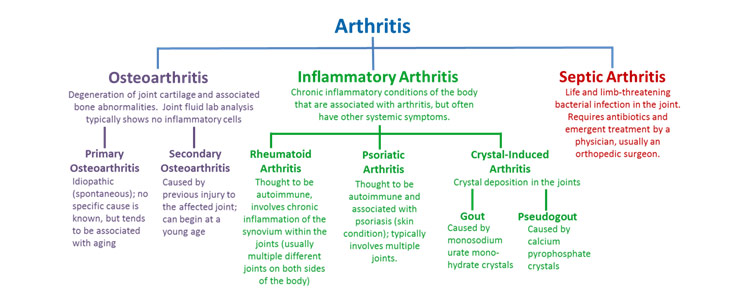
There are different types of arthritis:
- Degenerative Arthritis
-
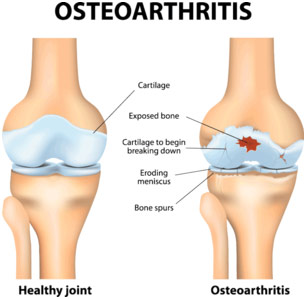
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis arthritis. When the cartilage – the slick, cushioning surface on the ends of bones – wears away, bone rubs against bone, causing pain, swelling and stiffness. Over time, joints can lose strength and pain may become chronic. Risk factors include excess weight, family history, age and previous injury (an anterior cruciate ligament, or ACL, tear, for example).
Osteoarthritis can prevented by staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding injury and repetitive movements.
-
- Inflammatory Arthritis
-
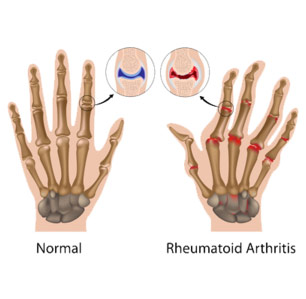
A healthy immune system is protective. It generates internal inflammation to get rid of infection and prevent disease. But the immune system can go awry, mistakenly attacking the joints with uncontrolled inflammation, potentially causing joint erosion and may damage internal organs, eyes and other parts of the body. Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are examples of inflammatory arthritis. Researchers believe that a combination of genetics and environmental factors can trigger autoimmunity. Smoking is an example of an environmental risk factor that can trigger rheumatoid arthritis in people with certain genes.
With autoimmune and inflammatory types of arthritis, early diagnosis and aggressive treatment is critical. Slowing disease activity can help minimize or even prevent permanent joint damage. Remission is the goal and may be achieved through the use of one or more medications known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). The goal of treatment is to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further joint damage.
-
- Infectious Arthritis
-
A bacterium, virus or fungus can enter the joint and trigger inflammation. Examples of organisms that can infect joints are salmonella and shigella (food poisoning or contamination), chlamydia and gonorrhea (sexually transmitted diseases) and hepatitis C (a blood-to-blood infection, often through shared needles or transfusions). In many cases, timely treatment with antibiotics may clear the joint infection, but sometimes the arthritis becomes chronic.
-
- Metabolic Arthritis
-
Uric acid is formed as the body breaks down purines, a substance found in human cells and in many foods. Some people have high levels of uric acid because they naturally produce more than is needed or the body can’t get rid of the uric acid quickly enough. In some people the uric acid builds up and forms needle-like crystals in the joint, resulting in sudden spikes of extreme joint pain, or a gout attack. Gout can come and go in episodes or, if uric acid levels aren’t reduced, it can become chronic, causing ongoing pain and disability.
-

